Writing Tests
Tests are placed inside of classes we lovingly call Test Bundles.
My First Test
class extends="testbox.system.BaseSpec"{
function run(){
describe( "My First Test", ()=>{
test( "it can add", ()=>{
expect( sum( 1, 2 ) ).toBe( 3 )
} )
} )
}
private function sum( a, b ){
return a + b
}
}component extends="testbox.system.BaseSpec"{
function run(){
describe( "My First Test", ()=>{
test( "it can add", ()=>{
expect( sum( 1, 2 ) ).toBe( 3 );
} );
} );
}
private function sum( a, b ){
return a + b;
}
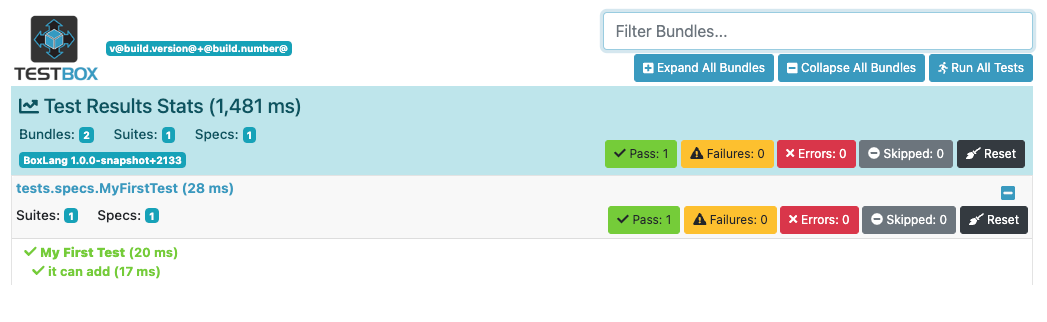
}
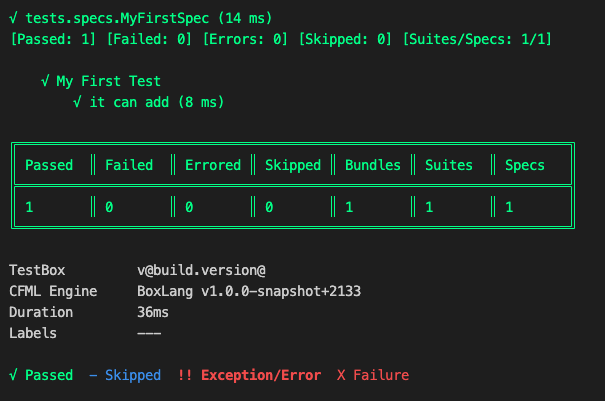
Optional Inheritance
Injected Variables
Injected/Inherited Methods
Quick Assertion Methods
Extension Methods
Environment Methods
Java Environment
Utility Methods
Mocking Methods
BDD Methods
Was this helpful?